2024
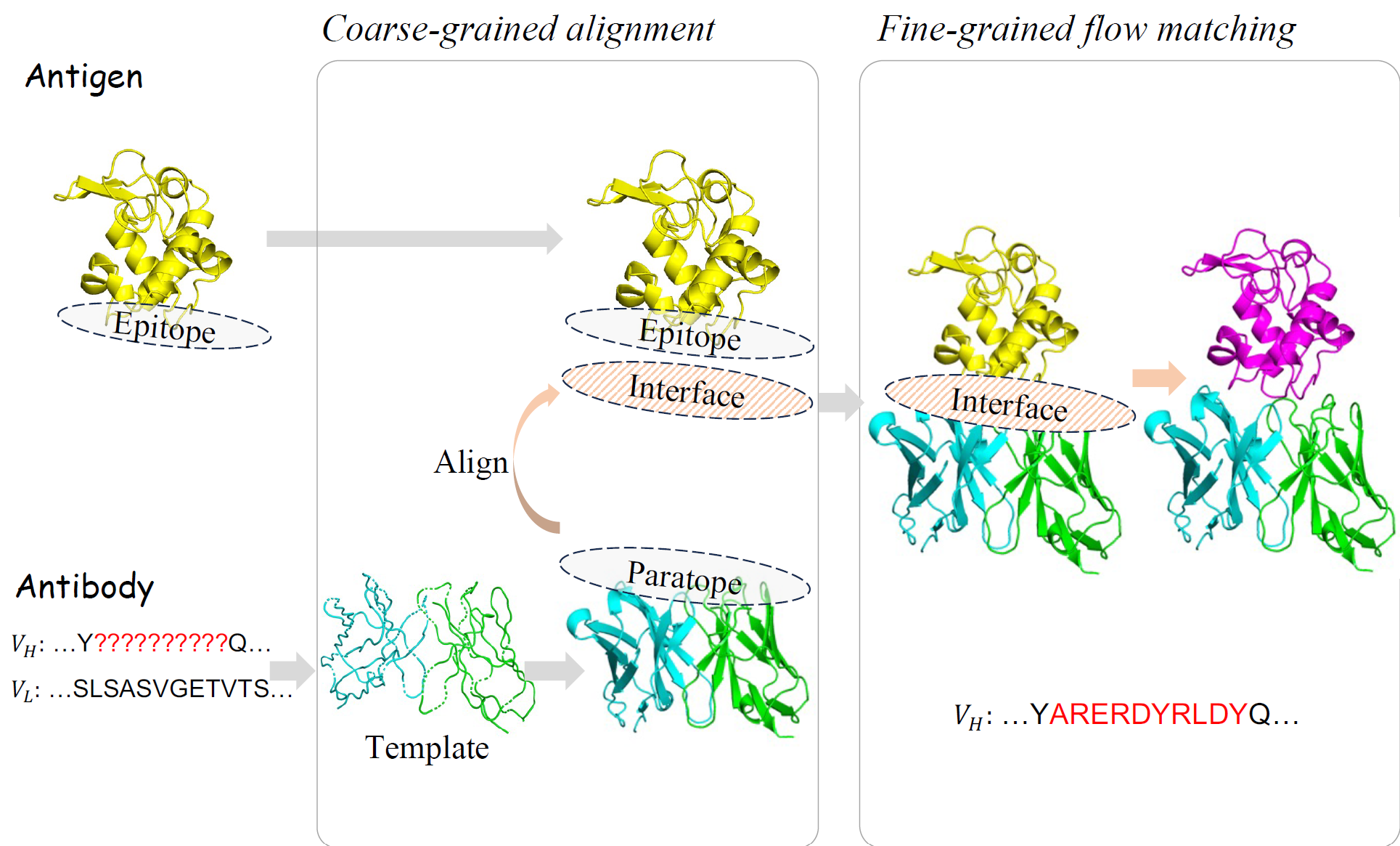
dyAb: Flow Matching for Flexible Antibody Design with AlphaFold-driven Pre-binding Antigen
Cheng Tan*, Yijie Zhang*, Zhangyang Gao*, Yufei Huang, Haitao Lin, Lirong Wu, Fandi Wu, Mathieu Blanchette#, Stan Z Li# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
The Thirty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) 2025 Oral Presentation
We introduce dyAb, a framework leveraging AlphaFold2-driven predictions and combining coarse-grained interface alignment with fine-grained flow matching to simulate dynamic interactions, significantly outperforming existing models and streamlining antibody design.
dyAb: Flow Matching for Flexible Antibody Design with AlphaFold-driven Pre-binding Antigen
Cheng Tan*, Yijie Zhang*, Zhangyang Gao*, Yufei Huang, Haitao Lin, Lirong Wu, Fandi Wu, Mathieu Blanchette#, Stan Z Li# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
The Thirty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) 2025 Oral Presentation
We introduce dyAb, a framework leveraging AlphaFold2-driven predictions and combining coarse-grained interface alignment with fine-grained flow matching to simulate dynamic interactions, significantly outperforming existing models and streamlining antibody design.
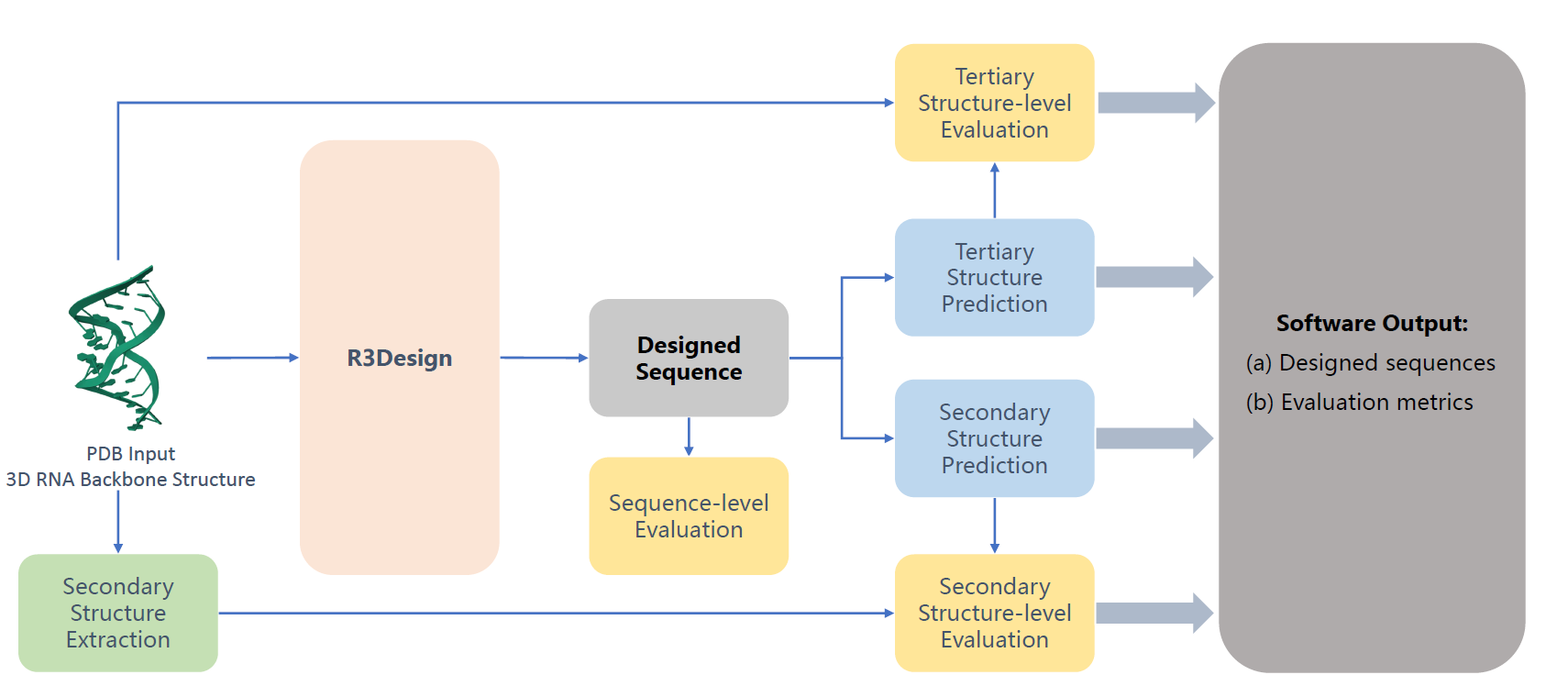
R3Design: Deep Tertiary Structure-based RNA Sequence Design and Beyond
Yijie Zhang*, Cheng Tan*, Zhangyang Gao*, Hanqun Cao, Siyuan Li, Siqi Ma, Mathieu Blanchette#, Stan Z Li# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2025
R3Design is a tertiary structure-based RNA sequence design method that prioritizes tertiary interactions, significantly outperforming traditional secondary structure-based approaches. By enabling the design, folding, and evaluation of RNA sequences that fold into desired tertiary structures.
R3Design: Deep Tertiary Structure-based RNA Sequence Design and Beyond
Yijie Zhang*, Cheng Tan*, Zhangyang Gao*, Hanqun Cao, Siyuan Li, Siqi Ma, Mathieu Blanchette#, Stan Z Li# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2025
R3Design is a tertiary structure-based RNA sequence design method that prioritizes tertiary interactions, significantly outperforming traditional secondary structure-based approaches. By enabling the design, folding, and evaluation of RNA sequences that fold into desired tertiary structures.
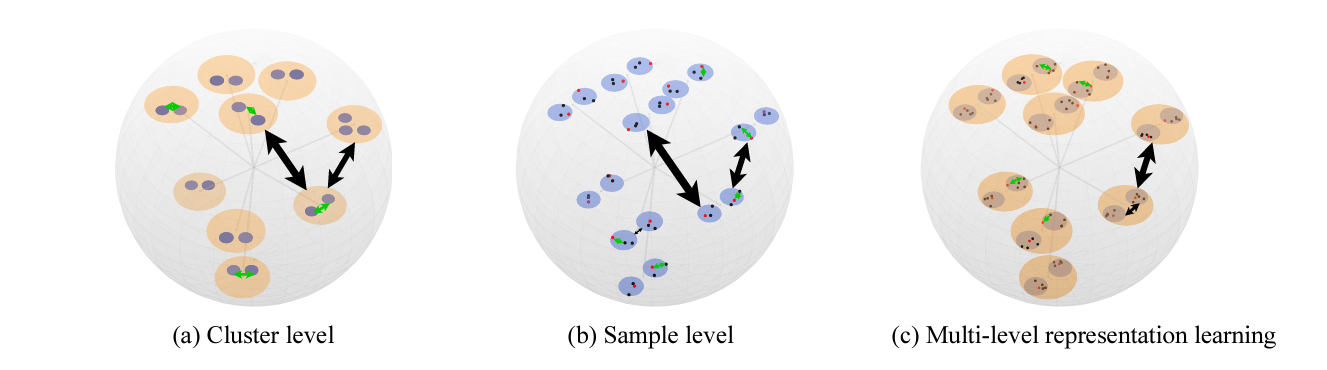
RDesign: Hierarchical Data-efficient Representation Learning for Tertiary Structure-based RNA Design
Cheng Tan*, Yijie Zhang*, Zhangyang Gao, Stan Z Li (* equal contribution)
The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) 2024
We proposed an RNA sequence design approach from the tertiary structure.
RDesign: Hierarchical Data-efficient Representation Learning for Tertiary Structure-based RNA Design
Cheng Tan*, Yijie Zhang*, Zhangyang Gao, Stan Z Li (* equal contribution)
The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) 2024
We proposed an RNA sequence design approach from the tertiary structure.
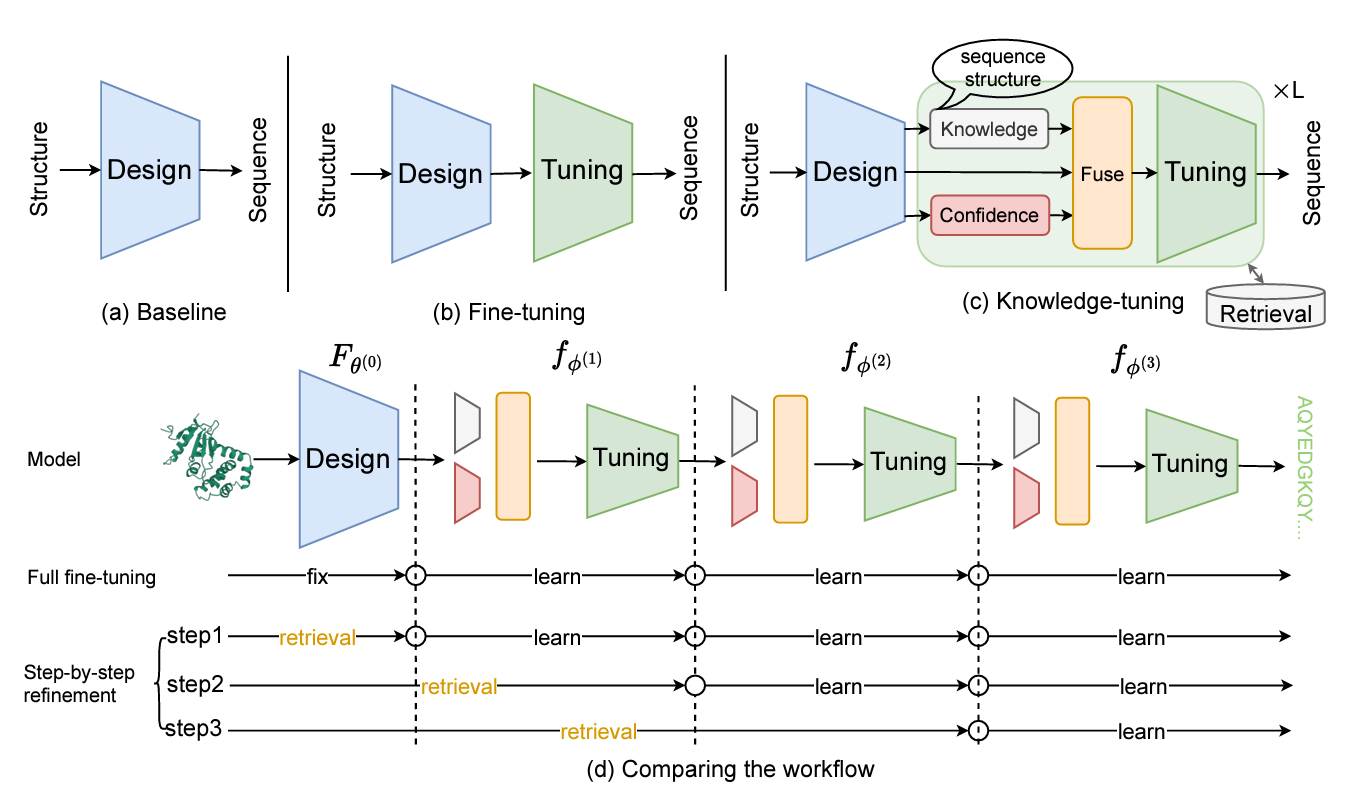
KW-Design: Pushing the Limit of Protein Design via Knowledge Refinement
Zhangyang Gao*, Cheng Tan*, Xingran Chen, Yijie Zhang, Jun Xia, Siyuan Li, Stan Z Li# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) 2024
Recent studies in protein design achieve competitive performance but often overlook predictive confidence, broad protein space coverage, and common protein knowledge. To address this, we propose KW-Design, a method that refines low-quality residues using a knowledge-aware module and accelerates training with a memory-retrieval mechanism
KW-Design: Pushing the Limit of Protein Design via Knowledge Refinement
Zhangyang Gao*, Cheng Tan*, Xingran Chen, Yijie Zhang, Jun Xia, Siyuan Li, Stan Z Li# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) 2024
Recent studies in protein design achieve competitive performance but often overlook predictive confidence, broad protein space coverage, and common protein knowledge. To address this, we propose KW-Design, a method that refines low-quality residues using a knowledge-aware module and accelerates training with a memory-retrieval mechanism
2023
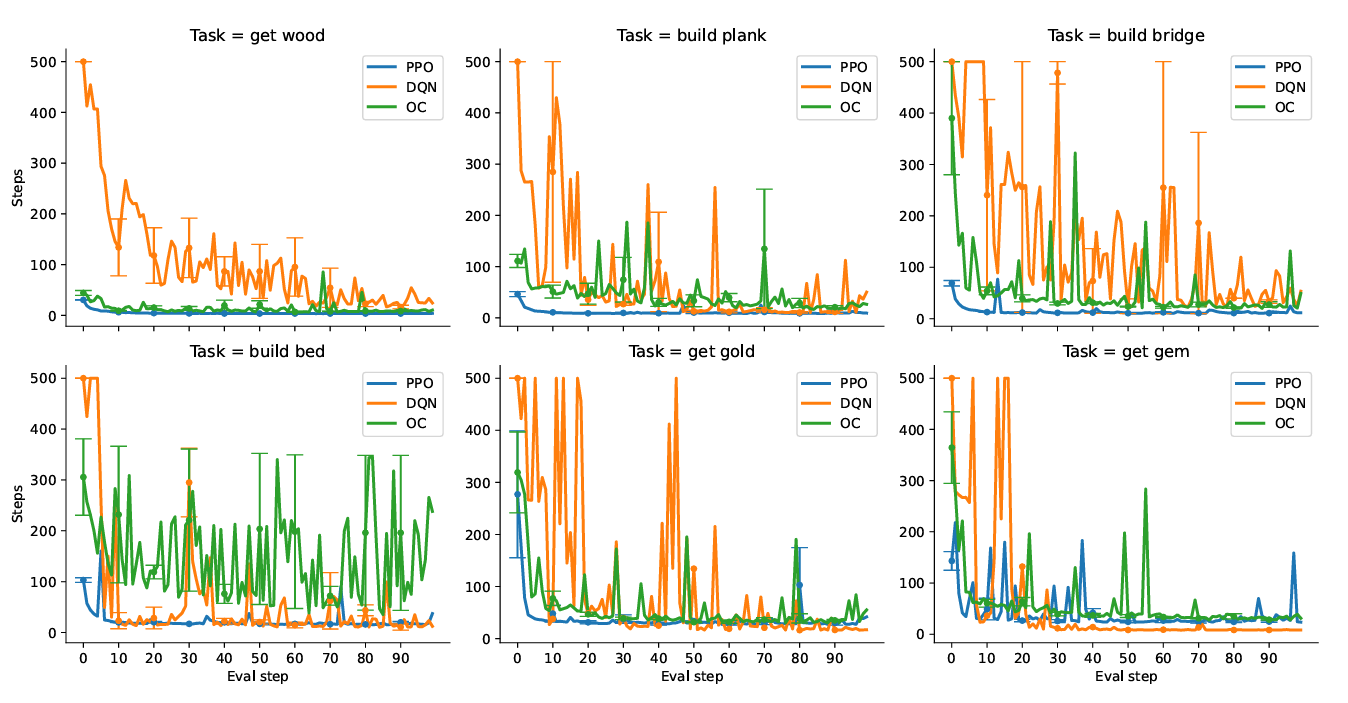
Does Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning Outperform Standard Reinforcement Learning in Goal-Oriented Environments?
Ziyan Luo*, Yijie Zhang*, Zhaoyue Wang* (* equal contribution)
NeurIPS 2023 Workshop on Goal-Conditioned Reinforcement Learning 2023
Our study reveals that HRL methods, without prior knowledge or well-structured rewards, do not consistently outperform standard RL methods, offering insights into their limitations in discovering effective goal-directed behavior.
Does Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning Outperform Standard Reinforcement Learning in Goal-Oriented Environments?
Ziyan Luo*, Yijie Zhang*, Zhaoyue Wang* (* equal contribution)
NeurIPS 2023 Workshop on Goal-Conditioned Reinforcement Learning 2023
Our study reveals that HRL methods, without prior knowledge or well-structured rewards, do not consistently outperform standard RL methods, offering insights into their limitations in discovering effective goal-directed behavior.
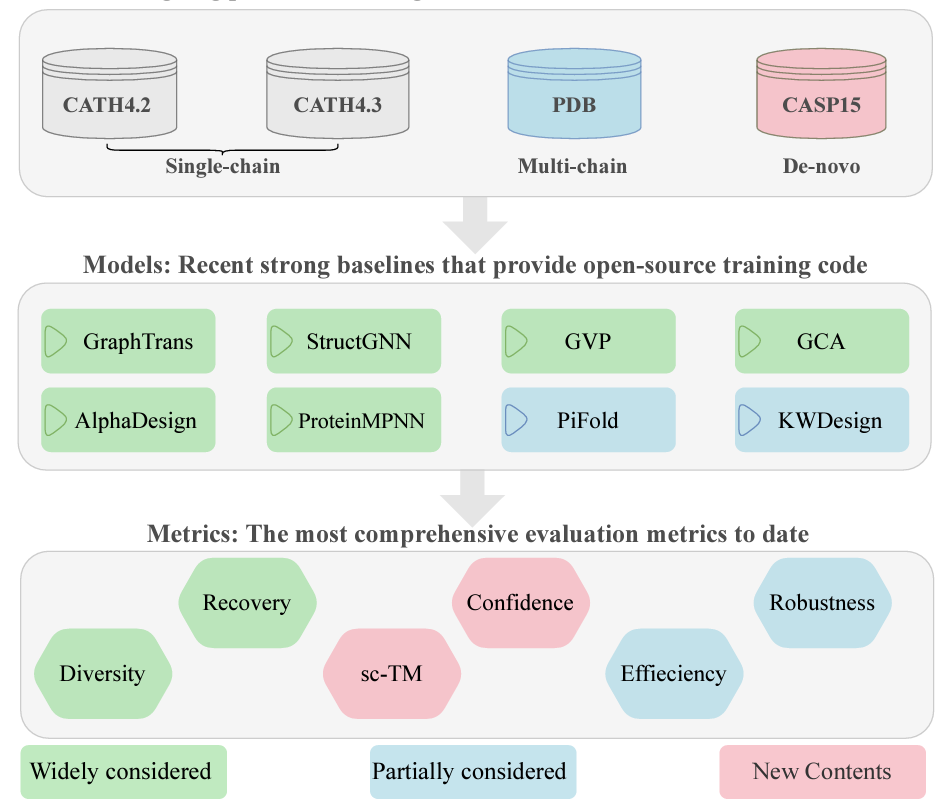
Proteininvbench: Benchmarking protein inverse folding on diverse tasks, models, and metrics
Zhangyang Gao*, Cheng Tan*, Yijie Zhang, Xingran Chen, Lirong Wu, Stan. Z Li# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (Neurips) 2023
Protein inverse folding has gained attention recently, but existing methods are limited by the CATH dataset, recovery metric, and lack of a unified benchmarking framework. To address this, we propose ProteinBench, a comprehensive benchmark integrating diverse protein design tasks, models, and evaluation metrics, enabling thorough comparisons and inspiring future advancements.
Proteininvbench: Benchmarking protein inverse folding on diverse tasks, models, and metrics
Zhangyang Gao*, Cheng Tan*, Yijie Zhang, Xingran Chen, Lirong Wu, Stan. Z Li# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (Neurips) 2023
Protein inverse folding has gained attention recently, but existing methods are limited by the CATH dataset, recovery metric, and lack of a unified benchmarking framework. To address this, we propose ProteinBench, a comprehensive benchmark integrating diverse protein design tasks, models, and evaluation metrics, enabling thorough comparisons and inspiring future advancements.
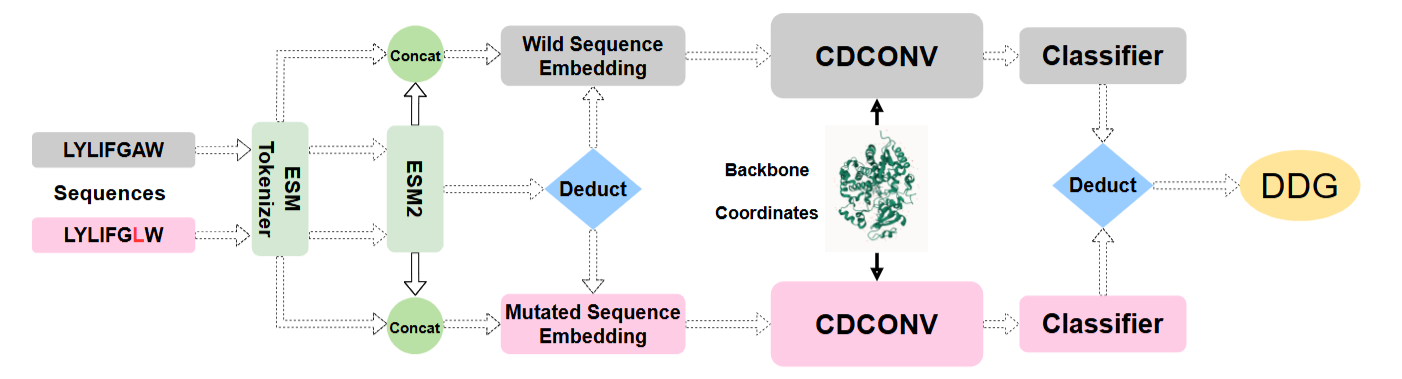
Efficiently Predicting Protein Stability Changes Upon Single-point Mutation with Large Language Models
Yijie Zhang, Zhangyang Gao, Cheng Tan, Stan Z. Li# (# corresponding author)
Arxiv 2023
Predicting protein stability changes from single-point mutations remains a significant challenge, hindered by feature extraction complexity and limited experimental data. Leveraging ESM-based large language models, we propose an efficient method integrating sequence and structural features to predict thermostability changes, supported by a carefully curated dataset to ensure fair model comparison.
Efficiently Predicting Protein Stability Changes Upon Single-point Mutation with Large Language Models
Yijie Zhang, Zhangyang Gao, Cheng Tan, Stan Z. Li# (# corresponding author)
Arxiv 2023
Predicting protein stability changes from single-point mutations remains a significant challenge, hindered by feature extraction complexity and limited experimental data. Leveraging ESM-based large language models, we propose an efficient method integrating sequence and structural features to predict thermostability changes, supported by a carefully curated dataset to ensure fair model comparison.
2022
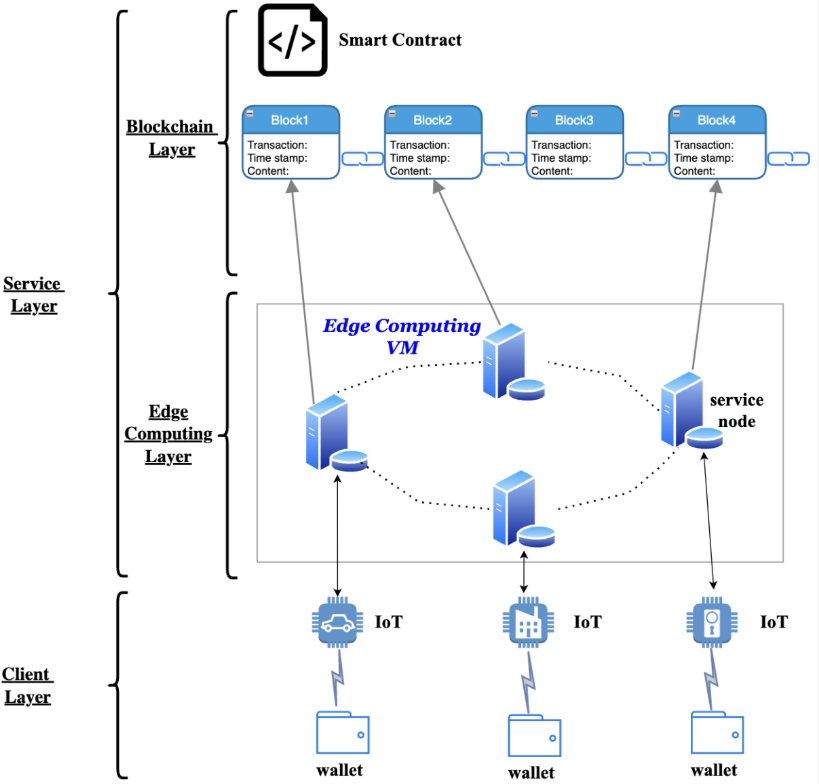
Resource allocation on blockchain enabled mobile edge computing system
Xinzhe Zheng, Yijie Zhang, Fan Yang, Fangmin Xu# (# corresponding author)
Electronics 2022
Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) addresses growing demands for high-quality computing, but traditional resource allocation faces challenges like privacy risks, further complicated by blockchain-enabled MEC systems. To tackle this, we propose a blockchain-based MEC architecture with a novel Proof of Learning (PoL) consensus, optimizing resource allocation using an A3C algorithm enhanced with temporal convolutional networks (TCN) for faster, more stable convergence.
Resource allocation on blockchain enabled mobile edge computing system
Xinzhe Zheng, Yijie Zhang, Fan Yang, Fangmin Xu# (# corresponding author)
Electronics 2022
Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) addresses growing demands for high-quality computing, but traditional resource allocation faces challenges like privacy risks, further complicated by blockchain-enabled MEC systems. To tackle this, we propose a blockchain-based MEC architecture with a novel Proof of Learning (PoL) consensus, optimizing resource allocation using an A3C algorithm enhanced with temporal convolutional networks (TCN) for faster, more stable convergence.